The Cheatsheet offers succinct code samples and explanations for typical coding contexts, making it useful for both experienced programmers and those in need of a quick refresher.
WHY USE A CHEAT SHEET FOR CODING?
Cheatsheets for coding are useful tools for programmers of all skill levels. When dealing with repetitive programming chores, they act as quick references to regularly used code snippets, saving time and effort. Our Java Cheatsheet tries to make your writing experience easier by giving succinct explanations and examples of common code patterns. For anyone interested in coding, this is part of how to become a junior developer: a beginners guide.
WHAT COMES WITH IT?
You may develop cleaner, more effective code by using this Java Cheatsheet, which includes key code snippets for frequent coding scenarios. It covers concepts including variable declarations, loops, conditional statements, arrays, methods, exception handling, file handling, streams, and ternary operators with examples and explanations.
USE OF THE CHEATSHEET
This Cheatsheet includes brief explanations for each code snippet to help you understand its use and purpose. Depending on your coding requirements, you can refer to the pertinent parts and incorporate the given examples into your projects with ease. Furthermore, feel free to expand on the examples to meet your particular needs.
A helpful tool for beginners is the Everyday code Cheatsheet for Java, which acts as a quick reference guide to typical code patterns. By offering succinct code snippets and explanations for typical coding scenarios, it tries to make your coding experience easier. This Cheatsheet will be a helpful companion whether you are just beginning your coding journey or just need a quick refresher.
Are you prepared to streamline your coding process? Let’s get started with the Java everyday coding Cheatsheet and improve your coding abilities!
DATA TYPES

VARIABLE DECLARATION

CONSTANT DECLARATION

ARRAY DECLARATION AND INITIALIZATION

OBJECT DECLARATION AND INITIALIZATION

METHOD DECLARATION

READING INPUT FROM USER

PRINTING OUTPUT

CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS – IF-ELSE STATEMENT

CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS – SWITCH STATEMENT

CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS – TERNARY OPERATOR
Expresses conditional logic in a single line

CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS – COMPARISON OPERATORS

CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS – BOOLEAN OPERATORS

LOOPING
FOR LOOP

WHILE LOOP

DO-WHILE LOOP

ARRAY MANIPULATION
ARRAY DECLARATION AND INITIALIZATION

ACCESSING ARRAY ELEMENTS

MODIFYING ARRAY ELEMENTS

STRING OPERATIONS
CREATING A STRING

CONCATENATING STRINGS
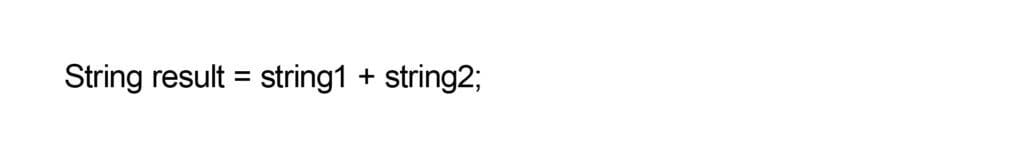
CHECKING STRING EQUALITY
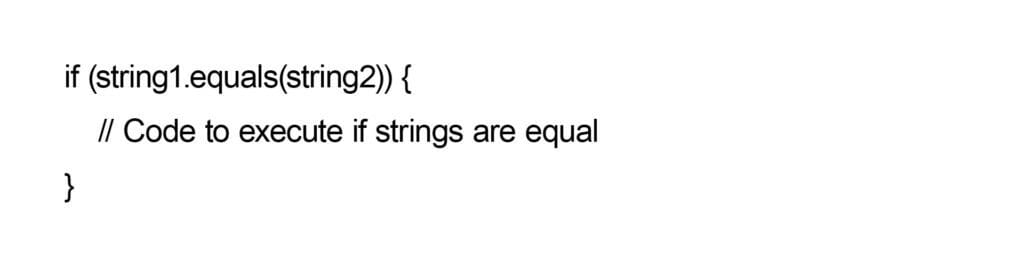
CONVERTING STRING TO INTEGER (NUMBER)

ANY TYPE TO STRING

STRING METHODS

MATHEMATICAL OPERATIONS
ADDITION

SUBTRACTION

MULTIPLICATION

DIVISION (QUOTIENT):

MODULUS/REMINDER OF DIVISION

INCREMENT/DECREMENT

EXCEPTION HANDLING

ARRAYLIST AND METHODS

HASHMAP AND METHODS

LAMBDA EXPRESSIONS
LAMBDA EXPRESSION DECLARATION

FOREACH LOOP

STREAMS
FILTER ELEMENTS

MAP ELEMENTS

REDUCE ELEMENTS

SORTING AND LIMITING

REDUCTION – SUM AND AVERAGE

DISTINCT AND COLLECT TO SET

Author: Dharshana Rammohan, Senior Developer at Apexon







